Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach used to identify the underlying cause(s) of a problem, failure, or defect. Instead of just addressing symptoms, RCA aims to find and eliminate the fundamental reason the issue occurred, preventing recurrence.
Key Principles of RCA
- Focus on Cause, Not Just Symptoms – RCA seeks to uncover why a problem happened, not just how it manifested.
- Data-Driven Approach – Uses evidence, facts, and logic rather than assumptions.
- Systematic and Structured – Follows a step-by-step methodology.
- Prevention-Oriented – Aims to implement corrective actions to avoid future occurrences.
RCA Process Steps
- Identify the Problem – Define the issue clearly (what happened, where, when, and how).
- Gather Data and Evidence – Collect relevant information, logs, reports, witness statements, etc.
- Determine Root Causes – Use analytical techniques to trace the issue back to its origin.
- Implement Corrective Actions – Develop solutions that address root causes rather than symptoms.
- Monitor and Verify Effectiveness – Ensure implemented actions prevent recurrence.
Common RCA Techniques
- 5 Whys – Repeatedly ask "Why?" to dig deeper into the root cause.
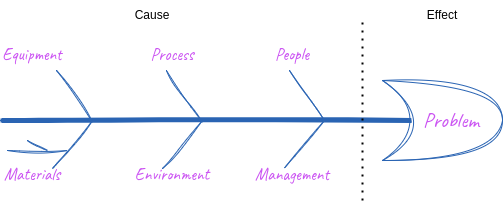
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa) – Categorizes causes into groups (e.g., People, Process, Equipment).
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) – Evaluates potential failure points systematically.
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) – Uses a logical tree structure to map out cause-and-effect relationships.
- Pareto Analysis – Identifies the most significant causes using the 80/20 rule.
Example of RCA in Action
Problem: A website experiences frequent downtime.
- Why? The server crashes.
- Why? High CPU usage overloads the system.
- Why? A poorly optimized database query is running continuously.
- Why? A recent software update introduced inefficient indexing.
- Why? The update was not thoroughly tested before deployment.
Root Cause: Inadequate testing process before software updates.
Solution: Implement a robust testing protocol before deployment.
References
- Five whys on Wikipedia
- Gitlab RCA template (Markdown)
Share on X (Twitter) Share on LinkedIn Share on Facebook